6b 2022 23/English: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Markierung: Quelltext-Bearbeitung 2017 |
Markierung: Quelltext-Bearbeitung 2017 |
||
| Zeile 375: | Zeile 375: | ||
=='''Exercises:'''== | =='''Exercises:'''== | ||
*[ | *[https://school-english.de/english/uebungen/6klasse/haveto1.htm müssen/nicht müssen 2] | ||
*[https://kico4u.de/english/uebungen/hilfsverben/havetrans.htm Müssen/nicht müssen 3] | *[https://kico4u.de/english/uebungen/hilfsverben/havetrans.htm Müssen/nicht müssen 3] | ||
Version vom 23. Juni 2023, 05:25 Uhr
Irregular verbs
Set 1A - B to D
to buy - bought() - bought()
to dig - dug() - dug()
to become - became() - become()
to cut- cut() - cut()
to build - built() - built()
to break - lost() - lost()
to draw - gave() - given()
to cost - cost() - cost()
to bet - bet() - bet()
Set 1B - B to D
to blow - blew() - blown()
to do - did() - done()
to begin - read() - read()
to bite - bit() - bitten()
to burn - burnt() - burnt()
to catch - caught() - caught()
to drink - drank() - drunk()
to choose - chose() - chosen()
to bring - brought() - brought()
to come - came() - come()
Set 2A - E to H
to find - found() - found()
to eat - ate() - eaten()
to hide - hid() - hidden()
to feel - felt() - felt()
to get - got() - got()
to go - went() - gone()
to find - found() - found()
to have - had() - had()
to give - gave() - given()
to fight - fought() - fought()
Set 2B - E to H
to hurt - hurt() - hurt()
to fall - fell() - fallen()
to freeze - froze() - frozen()
to grow - grew() - grown()
to forget - forgot() - forgotten()
to hear - heard() - heard()
to fly - flew() - flown()
to give - gave() - given()
to hit - hit() - hit()
to feed - fed() - fed()
Set 3A - K - "see"
to keep - kept() - kept()
to leave - left() - left()
to put - put() - put()
to run - ran() - run()
to pay - paid() - paid()
to hold - held() - held()
to lose - lost() - lost()
to say - said() - said()
to let - let() - let()
Set 3B - K to "see"
to ring - rang() - rung()
to meet - met() - met()
to see - saw() - seen()
to read - read() - read()
to hear - heard() - heard()
to mean - meant() - meant()
to know - knew() - known()
to make - made() - made()
to lie - lay() - lain()
to ride - rode() - ridden()
to let - let() - let()
Set 4A "sell to "write"
to write - wrote() - written()
to send - sent() - sent()
to sit - sat() - sat()
to speak - spoke() - spoken()
to teach - taught() - taught()
to sell - sold() - sold()
to wear - wore() - worn()
to sing - sang() - sung()
to say - said() - said()
to spell - spelt() - spelt()
to smell - rang() - rung()
to show - showed() - shown()
Set 4B "sell to "write"
to see - saw() - seen()
to win - won() - won()
to steal - stole() - stolen()
to take - took() - taken()
to throw - threw() - thrown()
to understand - understood() - understood()
to think - thought() - thought()
to set - set() - set()
to spend - spent() - spent()
to stand - stood() - stood()
to swim - swam() - swum()
to tell - told() - told()
Mündliche Schulaufgabe
Questions on the text
New Grammar
Going-to-future
- Form sentences in the "going-to-future"
- ... Amsterdam next week. (I, to fly to) I am going to fly to Amsterdam next week.
- ... basketball on Friday? (she/to play) Is she going to play basketball on Friday?
- ... their bikes at the weekend? (the boys/to ride) Are the boys going to ride their bikes at the weekend?
- ... his room today? (Paul, to clean) Is Paul going to clean his room today?
- ... you tomorrow morning! (I, to meet) I am going to meet you tomorrow morning?
- ... a new T-shirt on Saturday? (his mother/to buy) Is his mother going to buy a new T-shirt on Saturday?
- ... their friends at the station? (they/to meet) Are they going to meet their friends at the station?
- ... this terrible food! (I, not to eat) I am not going to eat this terrible food!
- ... her cat in the evening? (she/to feed) Is she going to feed her cat in the evening?
- ... your homework in the afternoon? (you/to do) Are you going to do your homework in the afternoon?
- ... a new boat in Scotland next year. (to buy, my parents) My parents are going to buy a new boat in Scotland next year.
- ... our parents? (they/to help) Are they going to help our parents?
Lösungen:
Zum Sichtbarmachen der Lösungen einfach die Lücken im Text (...) bzw. den Absatz mit der Maus einmal bzw. mehrmals (vom Webbrowser abhängig) anklicken oder markieren.
- Simple sentences in the going-to-future 1
- Simple sentences in the going-to-future 2
- Questions in the going-to-future 1
- Questions in the going-to-future 2
- Negative sentences in the going-to-future 1
- Negative sentences in the going-to-future 2
- Mixed exercise going-to-future
Question tags
- Form sentences with question tags
- He is Mara's brother ...? ...isn't he?
- We can't sleep at your house, ...? ... can we?
- You like this cheese, ...? ... don't you?
- Dad has got two brothers, ...? ... hasn't he?
- She's going to meet her friends in June, ...? ... isn't she?
- We play hockey after school, ...? ... don't we?'
- You aren't happy here, ...? ... are you?
- This isn't your bag, ...? ... is it?
Lösungen:
Zum Sichtbarmachen der Lösungen einfach die Lücken im Text (...) bzw. den Absatz mit der Maus einmal bzw. mehrmals (vom Webbrowser abhängig) anklicken oder markieren.
Questions with prepositions
- Deutsch: Auf wen wartest du? <= Präpostion am Satzanfang, nicht beim Verb!
- Englisch: Who are you waiting for? <= Präposition am Ende, direkt nach dem Verb! Fragewort am Anfang!
Form questions:
- She was listening to the music. What was she ... listening to?
- We came back with a friend. Who ... did you come back with?
- She comes from South Africa. Where does she come from?
- I'm interested in computers. What are you interested in?
- He is talking about dogs. What is he talking about?
- They are good at mathematics. What are they good at?
- He was looking for a job. What was he looking for?
- She was sitting on a nice chair. What was she sitting on?
- They are going to laugh about me! Who are they going to laugh about?
Lösungen:
Zum Sichtbarmachen der Lösungen einfach die Lücken im Text (...) bzw. den Absatz mit der Maus einmal bzw. mehrmals (vom Webbrowser abhängig) anklicken oder markieren.
Comparative and Superlative
Exercise: The Bragging Rapper
- to brag = angeben
- Fill the gaps! The words in bold print and the information in the brackets can help you!
- Write down the number in the bracket and the correct form!
You are big, but I'm so much ...... (1),
you think you're cooler than I, jo digga
but I am the ............. (2 - comparative of cool), guy here - harrgh
my car is so much .......... (3) than your car,
'cause you don't know what fast really means
you're not ..... (4) clever as my dog it seems!
I'm ......... (5 - comparative of sweet) ..... (6) sugar, my rap is ....... (7-form of "good") than yours
I drink Apfelsaftschorle - and that's ...... (8 - form of "nice") than Coors
I'm not as ............. (9 = groß) .... (10) a whale (=Walfisch), but cool
and I've got the ....................(11 - superlative of "fantastic") pool,
Listen, I'm much ..... ............ (12 - comparative form of "exciting") yes I
I am in this world the ......... .............. (13) guy!
Yeah , there is nobody more exciting than me .... nobody - man - more exciting than me ...
Exercises on comparative and superlative
- Comparisons with adjectives 0
- Comparisons with adjectives 1
- Comparisons with adjectives 2
- Comparisons with adjectives 3
- Comparisons with "as ... as"
- Comparisons with adjectives 4
Relative Pronouns and Relative Clauses
- Übung: Das richtige Relativpronomen 1
- Übung: Das richtige Relativpronomen 2
- Übung: Das richtige Relativpronomen 3
- Making relative clauses
Contact clauses:
Mixed exercises(more difficult):
Past progressive
- Verwendung: past progressive
- Übung: past progressive 1
- Übung: past progressive 2 - questions
- Übung: past progressive 3
- Simple past oder past progressive 1?
- Simple past oder past progressive 2?
- Simple past oder past progressive 3?
- Simple past oder past progressive 4?
- Simple past or past progressive 5?
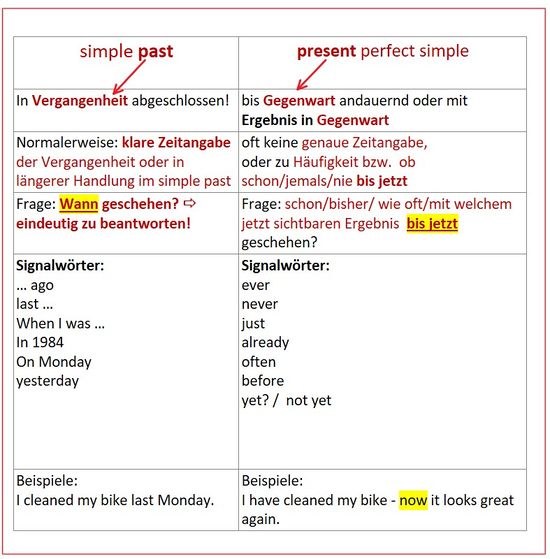
Present Perfect
Easy:
- Present Perfect: positive statements 1
- Present Perfect: positive statements 2
- Present Perfect: negative statements 1
- Present Perfect: negative statements 2
- Present Perfect: questions 1
- Present Perfect: questions 2
- Present Perfect: questions 3
Advanced:
Quite difficult:
Present Perfect or Simple Past?
Exercises
- Simple Past or Present Perfect - Exercise 0
- Simple Past or Present Perfect - Exercise I
- Present Perfect or Simple Past - Exercise II
- Present Perfect or Simple Past - Exercise III
- Present Perfect or Simple Past - Exercise IV
- Present Perfect or Simple Past - Exercise V
- Simple Past or Present Perfect - Exercise VI - difficult!
Erklärung
Can, may, must und Ersatzformen
Basic Rules
can, may, must sind Hilfsverben!
Das bedeutet:
- kein -s in der 3. Person Singular
- keine Umschreibung mit "to do" in Fragen und verneinten Sätzen notwendig (Can you help me? ABER Do you like me?)
Man kann mit can, may must nicht alle Zeiten bilden!
Ersatzformen:
- can ==> to be able to, ==> we were able to
- must ==> to have to ==> they had to do their homework
- may ==> to be allowed to ==> I was allowed to stay up.
Erlaubnis/Verbot = permission (dürfen/nicht dürfen)
- can / cannot ==> You cannot go to the party
- may / may not ==> we may not be loud ==> we were not allowed to be loud
- must not ==> you must not Du DARFST nicht (Nur in Gegenwart!) ==> Past Tense: You were not allowed to ....!
Fähigkeit = ability (können/nicht können)
- can / cannot ==> I cannot sing ==> I wasn't able to sing. / They weren't able to sing.
Verplichtung = obligation (müssen/nicht müssen)
- must ==> You must go. ==> You had to go.
Achtung: You must not heißt: Du darfst nicht!
Deswegen:
Du musst nicht gehen. ==> you needn't go. (Ersatzform für andere Zeiten: don't have to.
Deswegen
Du musstest nicht/brauchtest nicht zu gehen! ==> You didn't have o go.
Exercises: